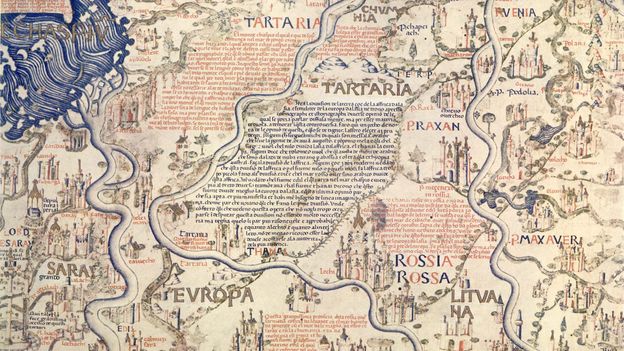
While the Hereford map depicted Heaven and Hell and was designed to serve as a compendium of the world’s knowledge from a spiritual perspective, Fra Mauro took a scientific approach to his cartography. He declared in his inscriptions that he would “verify the text by practical experience, investigating for many years and frequenting personas worthy of faith who have seen with their own eyes what I faithfully report here”.
There’s more than scientific and historical relevance to it, though. The most striking aspect of the map, which immediately catches your eye after ascending the white marble stairs of the Library of Saint Mark, where some of the world’s most precious and ancient manuscripts are kept, is its sheer splendour.
“It’s huge, beautiful, fantastically crafted,” said historian Pieralvise Zorzi. Beyond the outlines of countries and continents, Fra Mauro’s Mappa Mundi is a magnificent golden and blue painting composed of minute drawings of gorgeous palaces, bridges, sailing ships, rolling blue waves and outsized sea creatures, plus a total of 3,000 cartigli – red and blue annotations written in ancient Venetian that tell stories, anecdotes and legends.
In Norway, for instance, a cartiglio indicates the location where the Venetian merchant Pietro Querini came ashore after a shipwreck. As the tale goes, he not only survived the accident, but he brought stockfish back home, thus starting the Venetian passion for baccalà (the creamy fish spread you can find in every osteria).